Interactive Tables and Charts
Data Infrastructure
Space Force Tracked Debris in Orbit, June 2023
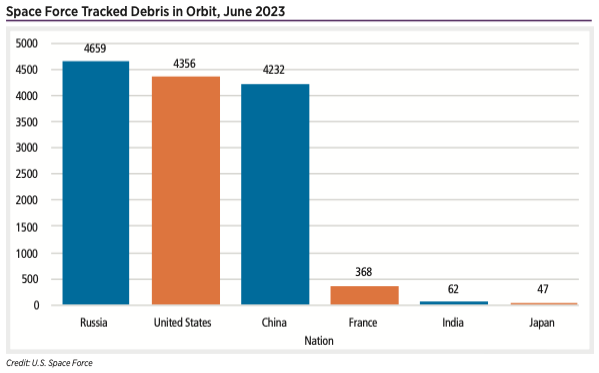
The Russians started it with pieces of Sputnik in 1957. America followed suit, and China is catching up in congesting low Earth orbit with clouds of debris that whiz around the planet at nearly 18,000 mph. Now, as low Earth orbit grows as a destination for massive constellations of satellites to deliver services from weather forecasts to phone calls, along with crewed commercial space stations, nations are racing to ban space-based littering and invent methods to take out the orbiting trash.
Select Launch Vehicles by Thrust
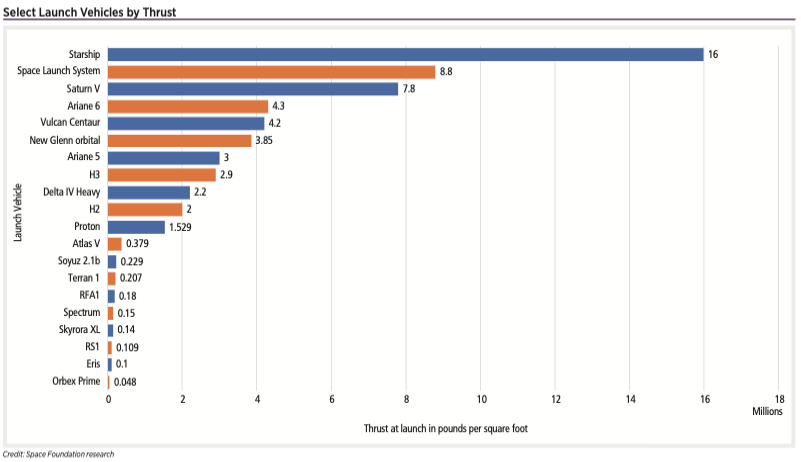
The European Space Agency (ESA), like NASA, is also using high-tech computer models to predict how these much more powerful rockets will behave. Learning on the fly with massive rocket boosters is a costly proposition.
Launches by Nation, 2014-2023
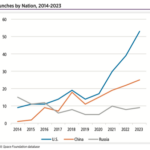
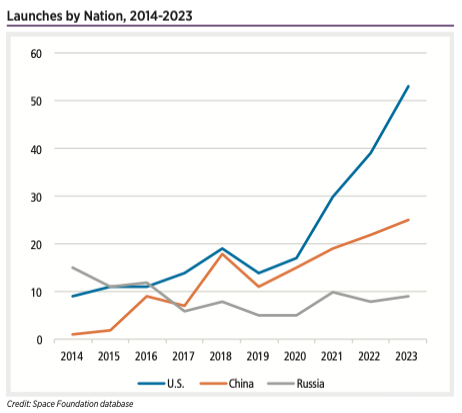
The second half of 2023 began with the launch of the European Space Agency’s Euclid telescope, designed to probe the universe’s dark matter. And several groundbreaking civil space missions remain on tap for the year.
Midyear Launch by Type, 2014-2023
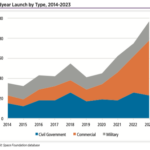
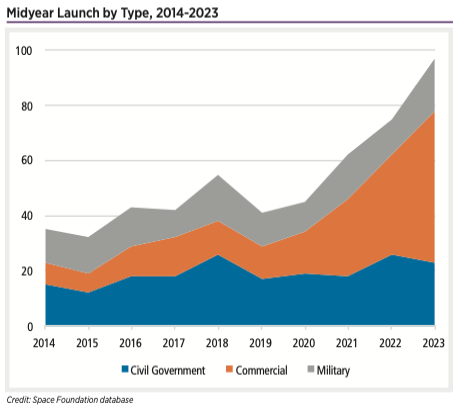
The failures pale in comparison to the successes, with a record 55 commercial launches through the midyear point. The first half of 2023 also set a midyear mark for military launches with 19 worldwide, exceeding the record of 17 set in the first half of 2018. Civil government launches were down slightly, with 23 launches in the first half of 2023, compared to 26 in the first half of 2022.
Midyear Launch Trends, 2014-2023
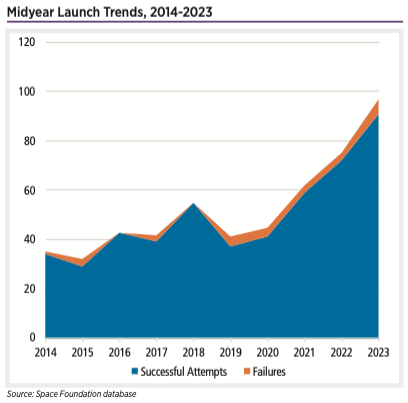
The first half of 2023 saw 97 launches worldwide, setting a record pace despite delays for major rocket programs that pushed the debuts of two major launch vehicles later into the year and notable failures on launch for SpaceX’s Starship in America and Mitsubishi’s H3 in Japan.
Launch Attempts by Top Operators, 2000-2022
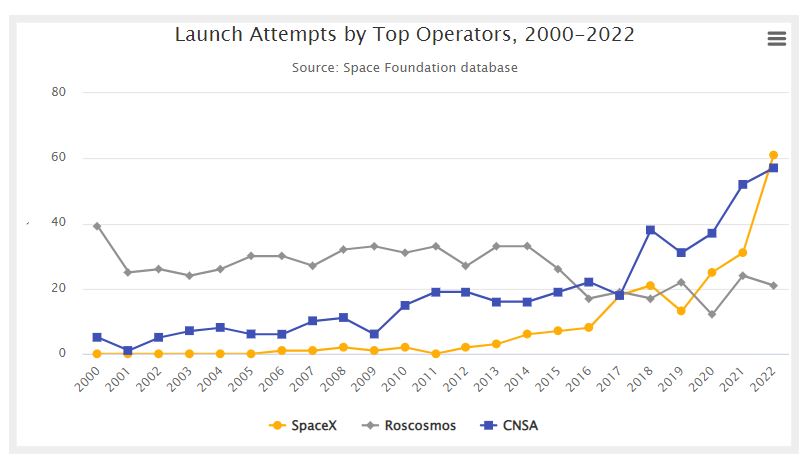
Two of the top three launch operators — CNSA and SpaceX — have contributed to overall launch activity growth by exponentially increasing their pace, while the third — Roscosmos — decreased its annual launches by 42% from 2000 to 2022.
Number of FAA Licensed and Permitted Operations Worldwide by Fiscal Year, 2015-2026
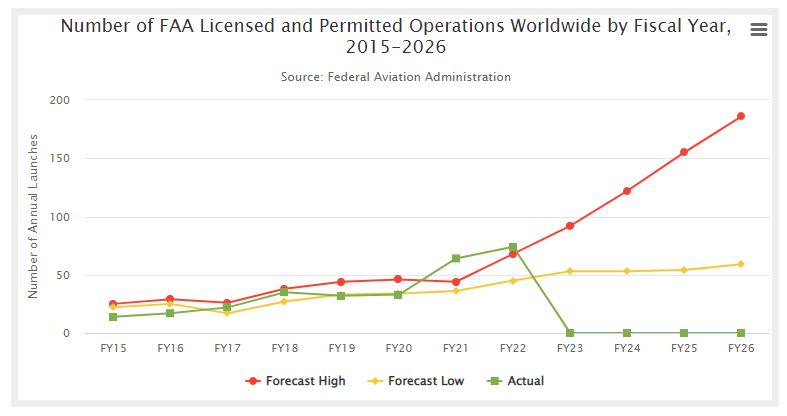
The Federal Aviation Administration’s (FAA) Office of Commercial Space Transportation and the Office of Spaceports have growing data supporting the rising pace of launches and the current strain on U.S. launch capacity.
International Spaceports Map
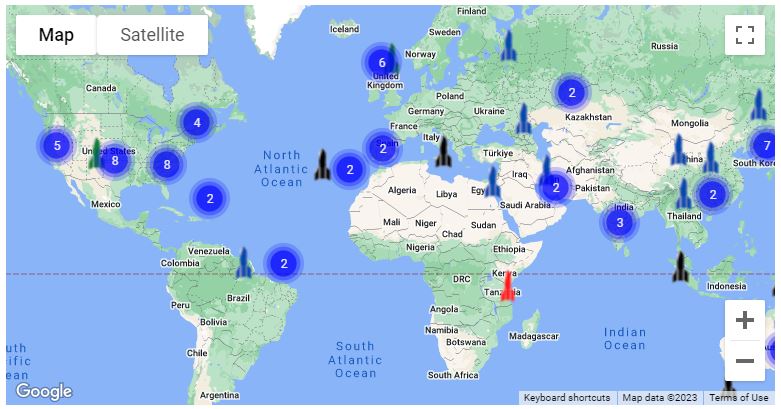
As the pace of small satellite development and global launches continues to accelerate, nations around the world are developing spaceport policies and courting launch providers and other space industries with the intent of expanding their access to space.
Per Nation Mass Share of an Estimated 973,000 KG, 2022
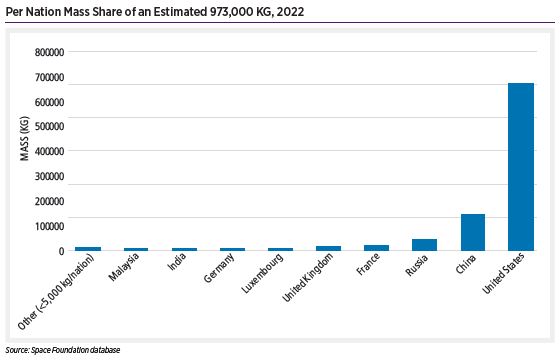
Operators deployed ~421 spacecraft with a mass of 200 kg or less, 18% of all deployed spacecraft in 2022. SpaceX’s Starlink satellites comprised over half the spacecraft mass deployed in 2022. The company’s Starlink deployments added up to 518,523 kg, nearly double the 257,140 kg it deployed in 2021. The largest spacecraft deployed during 2022 was Lockheed Martin’s Orion space capsule (25,848 kg), deployed during NASA’s first Artemis/Space Launch System launch.
Spacecraft Deployed Per Mass Range, 2022
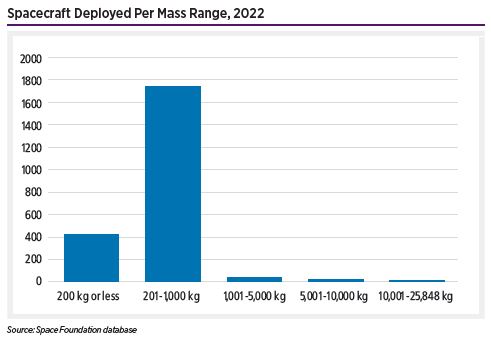
Mass estimates of all spacecraft deployed during 2022 exclude many of China’s spacecraft deployments and all U.S. classified spacecraft. However, without the mass totals from those two spacecraft operators, the overall spacecraft mass deployed during 2022 is estimated to be ~961,200 kilograms(kg), averaging ~415 kg per deployed spacecraft.