2014
NASA Civil Servant Workforce 2008-2017
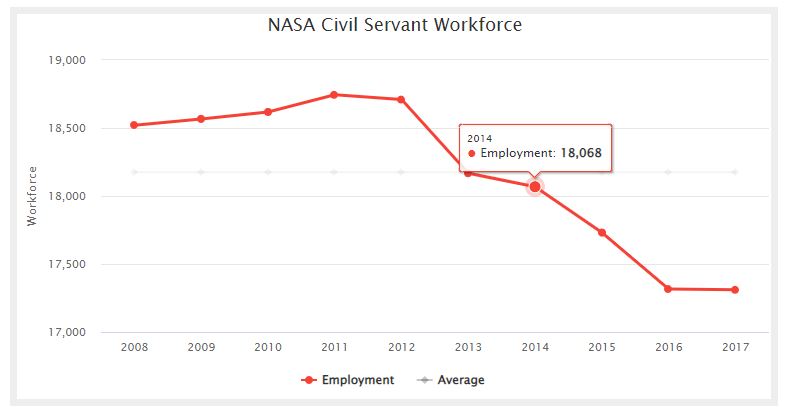
NASA Civil Servant Workforce chart showing the average and actual employment for the years 2008 through 2017.
Infrastructure: Space Infrastructure – TSR 2015
Products and Services: Space Products and Services – TSR 2015
Workforce: Space Workforce – TSR 2015
Economy: Space Economy – TSR 2015
2014 – Positioning, Navigation, and Timing Systems
Note: The exhibit in this section is from The Space Report 2015. Please refer to this year’s exhibits for the most current data as numbers may have been revised since this edition was published.
2014 – Iranian Suborbital
An example of a country using suborbital rockets for testing is Iran, which sent its second monkey into space in December 2013. Lifted aboard a Kavoshgar-e Pazhuhesh sounding rocket to an altitude of 120 kilometers (75 miles), the capsule containing the monkey parachuted safely back to Earth. The monkey, capsule, and rocket are part of Iran’s efforts to send a human into space by 2024.
2014 – Military Communications
Global, dedicated, and secure communications networks are vital to governments, militaries, and agencies around the world. Increased demand for capacity—particularly secure connectivity using non-commercial frequency bands—continued to drive deployment of dedicated military communications satellite systems. The U.S. military bought significant capacity from commercial operators such as Intelsat and SES in 2014. However, the way the military buys the bandwidth has been criticized by commercial satellite communications services as expensive and outdated.
2014 – Military Reconnaissance
While many remote-sensing and Earth observation satellites can be used for reconnaissance or other types of intelligence-gathering, military-specific and government-run satellites and sensor payloads are guided by very different mission requirements and laws than their commercial counterparts. There are several intelligence disciplines, or INTs, in which reconnaissance satellites are used to gain information: imagery intelligence (IMINT), signals intelligence (SIGINT), and measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT).
2014 – Meteorology
Weather satellites are a major segment of remote sensing satellites, using a mix of electro-optical, atmospheric, gravimetric, SAR, and other sensor payloads to detect fully formed weather systems as well as precursor conditions. Most weather satellites are in GEO or polar LEO orbits and have traditionally been operated by national governments for near-term weather forecasting and long-term climate modeling.