Canada
2014 – Canadian Government Space Budget
Canada’s FY 2014 budget, which began on April 1, 2014 and ended on March 31, 2015 included funding for civil space activities that totaled C$## million (US$## million). The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) is the only civil organization with a space budget line, so this total reflects its funding, which represents an ##% increase compared to FY 2013 funding of C$## million (US$## million). Other civil agencies that conduct space-related activities include the Department of Foreign Affairs, which provides Canada’s input to the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space; Transport Canada, which regulates spaceports and commercial space; and various stakeholders such as Natural Resources Canada, Environment Canada, and Agriculture Canada.
2014 – Government Space Budgets Overview
On a global level, government investment in space increased #% to $## billion. Because not all governments operate under the same fiscal cycle, space spending numbers were derived from the most recent budgetary information available for each country. As in previous years, the growth was not uniform, with some countries reducing the funding available for space activity, as shown below. The figures reported in the following country profiles are presented in both the local currency and U.S. dollars as of June 30 of the appropriate year.
Economy: Space Economy – TSR 2014
2013 – Government Space Budgets Overview
Government space programs accounted for approximately $## billion in spending during 2013, representing ##% of the global space economy. Government investment in space decreased by ##% in 2013, contributing to a cumulative average annual growth rate of ##% between 2009 and 2013. The top-line figures, however, do not fully depict how some countries have significantly increased space spending while others have made cuts, as shown in Exhibit 2n. Because not all governments operate under the same fiscal cycle, international space spending numbers were derived from the most recent budgetary information available for each country. The figures reported in the following country profiles are presented in both the local currency and U.S. dollars as of June 30 of the appropriate year.
2013 – Military Communications
Dedicated and secure communications links are vital to defense agencies around the world. Increasing demand for capacity—particularly secure connectivity using non-commercial frequency bands—has driven the deployment of dedicated military communications satellites. The U.S. military buys a significant portion of its capacity from commercial operators such as Intelsat and SES. However, the United States also relies on military-specific systems such as the Wideband Global SATCOM (WGS) program, supplying dedicated communications to U.S. and allied military forces around the globe.
2013 – Canada: Sapphire
The ability to minimize false detections of missile launches is a feature of Canada’s Sapphire spacecraft, launched in February 2013. The C$## million (US$## million) spacecraft, which features a unique orbit that positions it to track light reflected off of objects in space, offers space surveillance data to both Canada and the United States. Canada’s Sapphire satellite began contributing data on orbiting space objects to the Space Surveillance Network (SSN) system in January 2014.
2013 – Canadian Government Space Budget
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) received an FY 2013 budget appropriation of C$## million (US$## million). This figure included Canada’s planned C$## million (US$## million) FY 2013 contribution to the European Space Agency (ESA). The CSA-only budget, excluding ESA contributions, of C$## million (US$## million) represented a ##% increase from the previous year’s C$## million (US$## million).
2013 – Number of First-Degrees Awarded
The number of STEM first-degree (bachelor’s equivalent) graduates in many space-relevant countries has increased in recent years. The disciplines included here are physical, biological, and computer science; engineering; and mathematics.
2013 – PISA
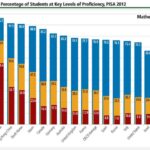
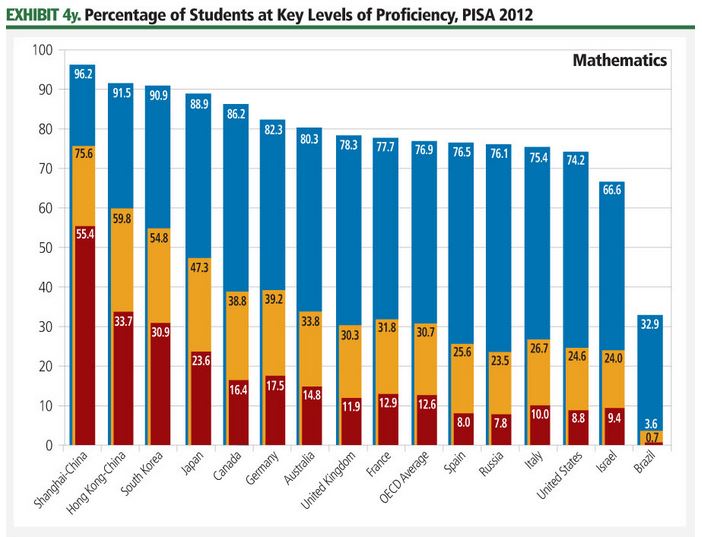
Trends in international primary and secondary STEM education can be compared across countries using two widely respected international exams. The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), carried out by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) every three years, focuses on the capabilities of 15-year-old students in mathematics and science literacy.
Canada’s Biopsy Robot
Advances in robotics led by space programs are finding a wide array of uses in the medical field. In addition to the hospital QC Bot derived from the Mars rovers, a robot capable of performing biopsies for breast cancer has been developed and is entering clinical trials.